This article is about ‘Concurrent Status Of Education’ in India. It answers the question ‘education comes under which list in India’. Education comes under a concurrent list and is a subject of concern for both State and central governments.
For B.Ed. students this topic concurrent status and education is studied under the subject Contemporary India and Education.
Concurrent Status of Education
The Constitution of India offers educational functions at three stages
- Central or union list
- State list
- Concurrent list
Until 1976, education was a state subject with some provisions at the central level. The 42nd amendment, 1976, was a about major and important changes to the Indian constitution. It also affected the status of education by putting it on the concurrent list.
Making education a concurrent subject ensures that both the centre and state can legislate on any aspect of education from primary to the university level.
In case of any dispute, legislation formed by the central government will have overriding authority. By having education in the concurrent list, centre can implement directly any policy decisions in the states.
So, concurrent status of education means that there is a partnership between State government and central government when it comes to Education policy making and implementation. This is a meaningful and yet a challenging task to accomplish.
Status of Education under three lists
Central/Union List
This list comprises of objects of great national interest. The Center has exclusive authority to legislate for the items of this list.
Entry 65
- Research centres for special studies
- Scientific or technical assistance in the investigation of detection of crime.
- Training of police officers, professionals, vocational or technical training
Entry 66
- Coordination and determination of standards in institutions for higher education or research and scientific and technical institutions.
- Establishment of university grant commission (UGC).
Entry 67
- Under article 49, protection of monuments and places and objects of National importance.
State List or Directive Principles of State Policy
The state list contains items pertaining to local interests, aims and objectives. The States have the right to legislate items on this List according to local preferences and objectives.
The Directive Principles of State Policy can be defined as guidelines to be followed in the governance of the country by the government. These values assist in providing policymakers and government officials with guidance and instructions to bear in mind when implementing policies. Some of the principles are in the form of social and economic rights
- Right to work
- Right to free and compulsory education of children upto age of 14.
- Right to equal wages for equal work, or right to adequate livelihood.
Even today these rights are not fully enjoyed by all Indian citizens.
In Directive principles,
- State looks after the interests of SC/ST
- State looks after public health, animal husbandry, prevent slaughter of cows and other milk giving animals, and to ban drinking.
- State looks after to promote cottage industries
- State should protect forests, wild life of the country and ancient monuments.
- States should follow policies to maintain peace in the country and in the world.
Education on the Concurrent list
Concurrent list encompasses items of concerns of both the centre and the states. Both will legislate for items in the concurrent List. Education is part of the concurrent List. This means policies related to education are legislated by central and state governments in the form of a meaningful partnership.
Education in concurrent list and its implications
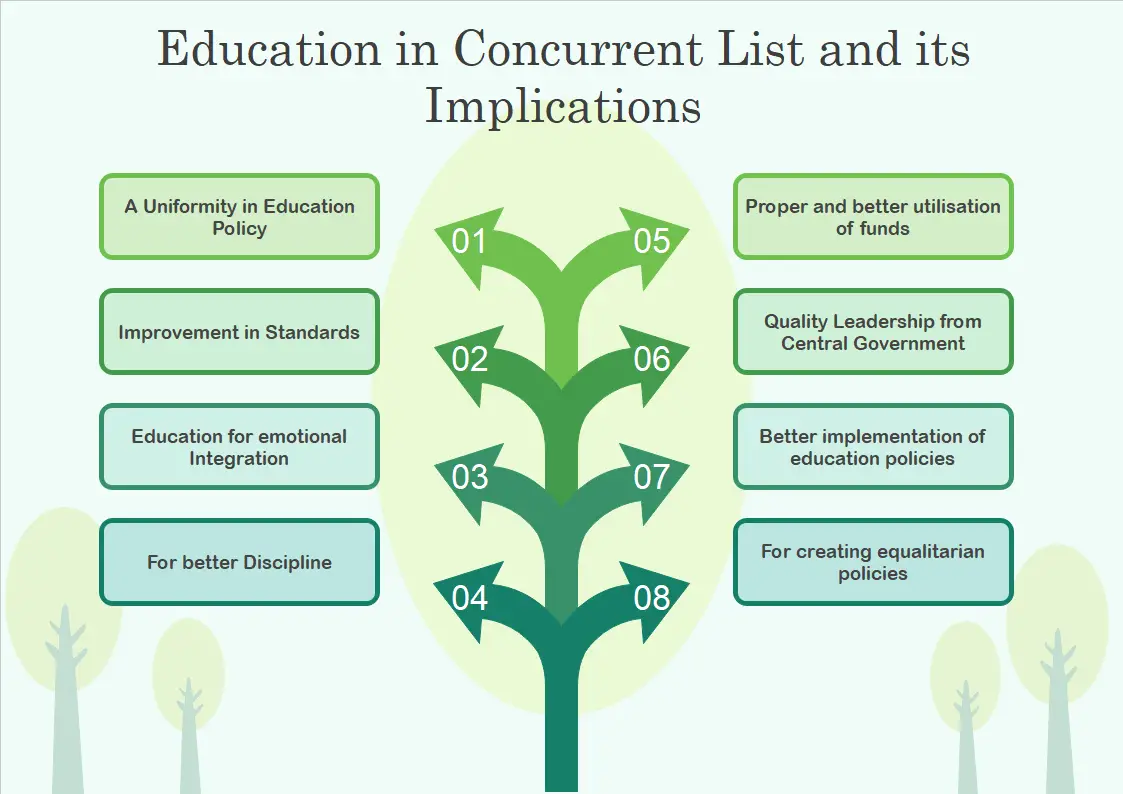
- A Uniformity in Education Policy: Education System and its pattern should be the same across all of India. This could only be possible when education is made a concurrent subject. This ensures that the structure of education does not vary from state to state.
- Improvement in Standards: As a result of education is a concurrent subject, research will advance throughout the nation. Due to this research studies are going to be utilized better at both state and national level.
- Education for emotional Integration: Education is the key force for the production of emotional integration between all of the country. Educational curriculum, strategies, goals, and priorities, etc. can include guidelines to both teachers and learners so that they can use them towards the purpose of emotional integration of the nation as a whole.
- For better Discipline: Central government has the power to overrule the decisions of state governments in case of disagreements. This power is given to central for maintaining better discipline when it comes to maintaining standards of education and better emotional integration throughout the country.
- Proper and better utilization of funds: The state receives funding from the center for education but sometimes they spend it elsewhere, as has been noted. The center must have a say in its use when the funds are distributed by the central government for the betterment of schools and the education infrastructure of states.
- Quality Leadership from Central Government: Sometimes central government is able to provide quality leadership in the form of direction and supervision when it comes to the matters of education.
- Better implementation of education policies: Better implementation of policies related to education means the better implementation of education policies in a systematic way for better results. If education is on the concurrent list, the center will ensure that state governments are correctly implementing it.
- For creating equalitarian policies: Our constitution provides equal rights to each and every citizen in the society. For achieving equity and equality in society education must be provided to all, as the constitution gives the right to education to all.
