Kothari Commission is also known as the Indian Education commission was appointed by the government of India towards the end of the third five-year plan. This commission was headed by Dr. Kothari.
Purpose of appointing education commission
In order to remove the defects in the field of education, the government appoints a new education commission to advise the government on the national pattern of education along with general principles and policies for the development of education at all stages. This commission was built in 1964-66 under the guidance of the Indian Constitution.
Learn more about the Indian Constitution and Education.
Educational defects at that time
Major educational defects that existed in the education system were
- Inadequate importance to agriculture
- Not connected with national reconstruction
- Too much academics
- No emphasis on character formation.
In this report, the commission expressed its firm belief that education is the most powerful instrument of national development.
Kothari Commission Report
Kothari Commission report is divided into four sections
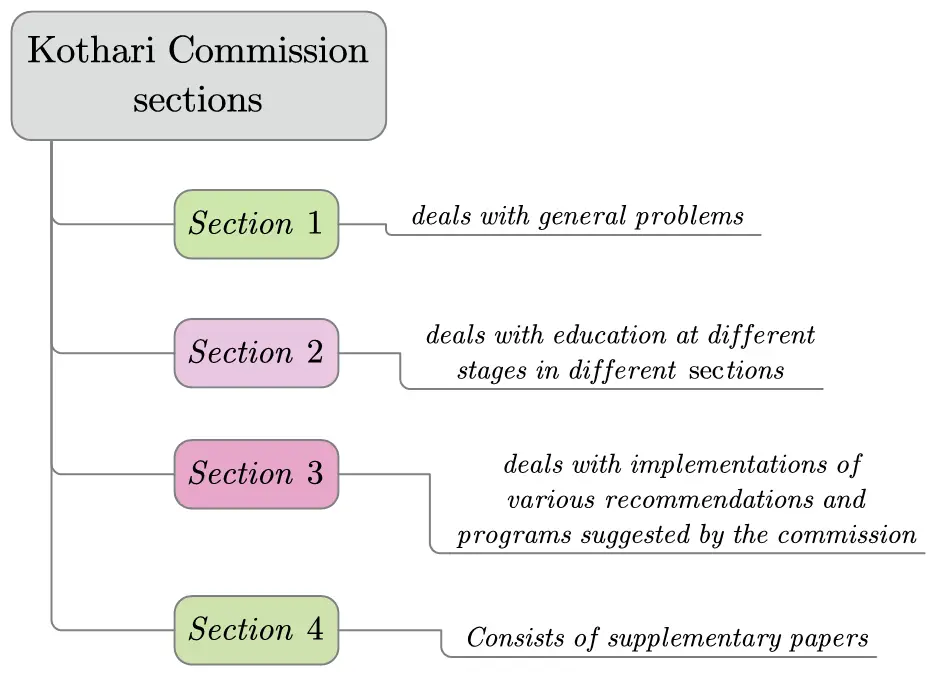
Commission feels that no reform is important or more than to transform education and relate it to the life, needs, and aspirations of the people. This can be done by
- Relating education to productivity.
- Strengthening social and national integration
- Accelerating the process of modernization
- cultivating social, moral and spiritual values.
Kothari Commission Recommendations
Curriculum related recommendations
- Research in the curriculum that should be done by universities and state education boards in order to upgrade it
- Emphasis on science education –
- science/maths compulsory for the first 10 years of education
- link science with technology in urban areas and with agriculture in rural areas
- Preparation of advanced curricula – The commission suggested state boards of education prepare advanced curricula in all subjects. It advised boards to introduce such curricula in phases so that it can fulfill the conditions of staff and provide facilities.
- An effective program of social studies as it is good for citizenship and emotional integration.
- Special plan for teaching languages – Three languages (mother tongue, Hindi and English) should be studied from class 8th but not on a compulsory basis
- Education in moral and spiritual values – Suggested making organized attempts for imparting moral education and including spiritual values.
- The new curriculum and basic education – According to commission
- Education must be a productive activity
- There must be a relationship between curriculum and environment
- There should be a connection and contact with local communities. This is important because it enables in shaping the education system at all levels.
- Social service programs – Such programs and participation in community development should be organized at different levels in an age-appropriate manner.
- Emphasis on mathematics
Areas of curricular studies for secondary stage
In view of the commission secondary stage can be studied under two categories :
Lower secondary stage – Class viii to x
- In Non-Hindi speaking areas
- The mother tongue or regional language
- Hindi at a higher or lower level
- English at a higher or lower level
- In Hindi speaking areas
- The mother tongue or regional language
- English
- A modern Indian language other than Hindi
- Mathematics
- Science
- History, geography and social science
- Art
- Work Experience and social service
- Education in moral-spiritual values
Higher Secondary stage
- Any two languages including any modern Indian language or any classical language.
- Any three subjects from the following list
History Sociology Geography Art Economics Physics Logic Chemistry Psychology Mathematics Geology Biology Home Science – - Work experience and social service
- Physical Education
- Art or craft
- Education in modern and spiritual values
Visit page Contemporary India and Education for more such topics.

Thank you for the notes
It’s help me alot