From this article Knowledge: meaning, types and sources , we already have an idea what is knowledge?
In this article we’ll learn about Methods of acquiring knowledge or we can say different ways of knowing knowledge.
Philosophers and educationists have bought out specific methods of acquiring knowledge. Thus there are different ways of knowing knowledge.
Before going any further let us have a brief recap of knowledge. So what is Knowledge?
- From the Indian point of view, knowledge is named as Vidya. It involves facts about reality as well as cognitive changes.
- Knowledge, as defined by Oxford dictionary, is
- What is known in a particular field
- Awareness gained by experience of fact or situation
- The theoretical and practical understanding of a subject.
- Religious Interpretations:- Various religions have interpreted knowledge differently
- Hindu Scriptures presents two kinds of knowledge:-
(A) Paroksh Gyan:- It is second-hand knowledge obtained from books, hearing lectures etc.
(B) Aproksha Gyan:- It is knowledge obtained by direct experiences. - According to Quran Knowledge comes from God and various habits encourage the acquisition of knowledge.
- According to Christianity Knowledge is one of the seven gifts of the Holy Spirit.
- Hindu Scriptures presents two kinds of knowledge:-
Some methods of knowledge acquisition are given below:-
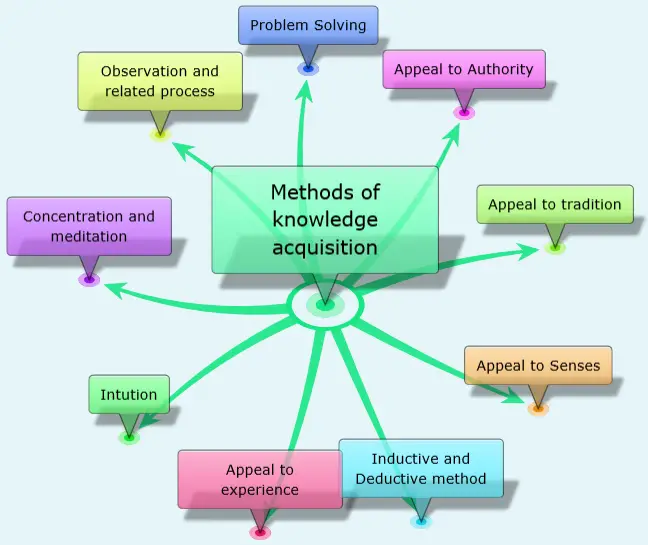
Let us now have an explanation of them one by one:-
- Appeal to authority:-
- Comes from authority or specialist in a particular field of knowledge.
- For example scientists, philosophers, professor, economists etc.
- Teachers are accepted as an authority and great source of knowledge by learners.
- Appeal to Tradition:-
- W depend on our traditions for the solution of many problems we might face in our life.
- So, we have accepted various traditions of our forefathers or our culture.
- Everything that we have accepted from our traditions might not always be valid.
- Over the period of time, people have rejected those wrong traditions which were once valid.
- Therefore we should always evaluate the knowledge acquired from traditions before accepting it.
- Appeal to Senses
- Knowledge is drawn through five senses.
- The more the senses are involved in process of acquiring knowledge, more comprehensive would be the knowledge acquired.
- Inductive and Deductive methods:-
- The inductive method starts with particular examples. Here learner tries to arrive at a certain conclusion. This may lead to the formulation of a law, generalization or principle.
- In deductive method learner starts with a generalization or rule, then he comes to particular examples.
- So we can say that knowledge is gathered both by inductive and deductive methods.
- Appeal to experiences:
- Knowledge can also be gathered by experiences.
- Our personal experiences or experiences of other people are the most familiar and fundamental sources of knowledge.
- We learn many things from our day to life and what goes around us.
- Intuition:-
- The knowledge gained out of intuition is spontaneous and sudden.
- Senses and mind are not involved during intuition.
- Anyone can experience it at different points of time.
- Concentration and meditation:-
- Concentration is a mental activity where the person concentrating focuses his mental energy on aids like a candle flame, idea. breathing, mantras etc.
- In meditation person meditating concentrates for a longer period of time. Both of them are foundations of attaining knowledge.
- While meditating or concentrating a person can make inferences. He can even make a link of facts of knowledge to something meaningful.
- Observation and related processes:-
Four sub-processes of attaining knowledge are observation, explanation, prediction and control.- Observation can be internal or external. It can even be a scientific observation.
- An explanation is the elaboration of facts of knowledge in a logical manner.
- Prediction is a process related to cause and effect. In this process, results are predicted. One needs to understand about causes and their effects.
- Control is the process in which results are filtered out by exercising control on certain factors.
- Problem Solving:-
Here the solution of the problem being solved becomes the part of knowledge. So, problem-solving is also an effective tool to acquire knowledge.
Related Articles
the distinction between knowledge and knowing (a forum link)How To Acquire Knowledge
14 Ways to Acquire Knowledge: A Timeless Guide from 1936
