- Palaeontology
- Comparative Anatomy and Morphology
- Molecular Homology
- Biogeography
Palaeontology:
The study of fossils is known as Palaeontology. Father of palaeontology is Leonardo da Vinci.
Fossils found in the rock support organic evolution. Rocks are formed by sedimentation and a cross section of earth crust indicates the arrangement of sediments of different ages of different life forms which probably died during the formation of particular sediment.
By studying fossils following facts about organic evolution are evident:
- Fossils found in older rocks are of simple types those found in newer rocks are of complex type.
- In the beginning unicellular protozoan were formed from which multicellular organisms evolved.
- Some fossils represent connecting link between two groups and other show transitional state between 2 species.
- Angiosperms among plants and mammals among animals are highly developed and modern organisms.
- By fossils we can study the evolutionary pedigree of an animal like in evolution of horse, man, elephant etc.
Age of Fossils:
The age of the fossils can be determined by “Radioactive Dating” which is based on the conversion of unstable radioactive nuclei into stable nuclei overa fixed period.
Electron spin resonance (ESR) method is a relatively most accurate method of dating of fossils.
Examples:
- Ichthyosaurs were extinct fish-like reptiles which lived in the ocean.
- Pterosaurs were extinct bird-like flying reptiles.
- Archaeopteryx lithographica was a jurassic fossil bird having reptilian characters. It is a connecting link or transitional stage between reptiles and birds as it possesses both reptilian as well as avian characters.
Comparative Anatomy and Morphology:
Homology and Homologous Organs:
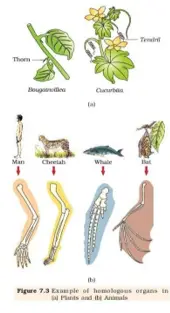
Homologous organs are those organs which have a common origin and are built on the same basic pattern but perform different functions ard are modified accordingly.
Examples:
- Limb skeleton of vertebrates. Forelimbs of whales (flippers), bats (wings), cheetah and human are all homologous organs. They are constructed on the same pentadactyl pattern consisting of almost the same bones i.e., humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges.
- In plants, thorn of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita.
Homologous organs are found in forms showing adaptive radiation from a common ancestor; so these give evidence of ‘Divergent Evolution’.
Analogy and Analogous Organs:
It is similarity in organs based on similar functions. Organs which have different origins and dissimilar fundamental structure but have similar functions are called analogous organs.
Examples:
Wings of bats , birds and wings of insects.
Fins of fish, flippers of seal and paddles of whale.
Sweet potato and potato
Chloragogen cells of Pheretima and liver of vertebrates.
Eyes of Octopus and mammals
Analogy is the result of convergent evolution where similar habitat conditions have selected similar adaptive features in different group of organisms towards the same functions.
When adaptive convergence is found in closely related species is called ‘parallel evolution’.
Molecular homology:
It refers to the similarities in the biomolecules of different organisms. The biomolecule similarity point to the same or common ancestry of diverse organisms.
Evidences from Bio-geography:
The different geographical distribution of different group of organisms also indicate common shared ancestry in that respective regions.
Habitat isolation has probably restricted these organism to a particular geography on the earth
