Watson and Crick had prepared a scheme for replication of DNA when they proposed the double helical structure of DNA.
The scheme suggested that the two strands would separate and each act as a template for synthesis of new complementary strand.
After complete replication each DNA molecule would have one parental and one newly synthesized strand.
This scheme is termed as semi- conservative DNA replication.
Experimental Proof of Semi-Conservative Replication of DNA:(Meselson and Stahl Experiment)
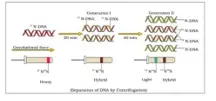
Mathew Meselson and Franklin Stahl have performed an experiment using E. coli to prove that DNA replication is semi conservative.
- They grow E. coli in a medium containing 15NH4Cl until 15N wa incorporated in the two strands of newly synthesized DNA.
- This heavy DNA can be separated from normal 15N DNA by centrifugation in CsCl2 density gradient.
- Then they transferred the cells into a medium with normal NH4Cl and took out samples at various time intervals and extracted DNA and centrifuged them to measure their density.
- The DNA from cells after one generation of transfer from the 15N medium to 14N medium (i.e., after 20 mins) i.e., had an intermediate/hybrid density.
- The DNA extracted after two generation that is after 40 minutes consisted of equal amount of light DNA and hybrid DNA.
- Similar experiments were conducted by Taylor et al in 1958 by using radioactive thymidine. They prove that DNA on the chromosome replicate in a semi conservative manner
Mechanism of DNA Replication:
- The process involves number of enzymes/ catalyst of which the main enzyme is DNA dependent DNA polymerase that catalyzes the polymerization of deoxyribonucleotide at the rate of 2000 base pair per second.
- The process is also an energy expensive process, deoxynucleotides triphosphate (dNTPs) serve the dual purpose of: Acting as substrate, Providing energy
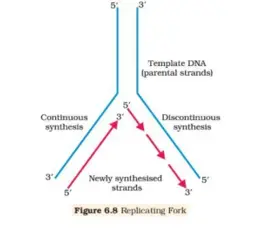
- The interwine strand of DNA separates from a particular point called origin of replication.
- Since, the two strands cannot be separated in its entire length (due to very high energy requirement) replication occurs with small opening of the DNA helix, the Y- shaped structure is formed called replication fork.
- Unwinding of DNA molecule is done by the help of enzyme helicases and topoisomerases.
- The DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyzes polymerization of nucleotides only in 5′ – 3′ direction.
- Consequently, on one of the template strand (with 3′ – 5′ polarity), the synthesis of DNA is continuous (leading strand).
- While on the other templates with polarity 5′ – to 3′ the synthesis of DNA is discontinuous (leggings strand) that is stretches of DNA are synthesized. The small segment of DNA are call okazaki segments.
- The Discontinuously synthesized strands are later joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Proof Reading and DNA Repair:
- The specificity of base pairing ensure the exact replication.
- Somehow it is possible that the wrong bases may get in at a frequency of 1 in 10000. This wrongly introduced bases can be removed by the activity of enzyme DNA polymerase.
- Even the wrong bases entered into the Helix of DNA by mutation (escape by proofreading mechanism of DNA) can be identified and corrected by repair enzymes.
Q. Write the name of the enzymes involved in DNA replication?
Ans. Enzymes involved in DNA replication are:
- DNA helicase
- Topoisomerase
- DNA dependent DNA polymerase
- RNA primase
- DNA ligase
