Ribonucleic acid was the first genetic material. The 2′-OH of nucleotide is a reactive group that makes RNA catalytic.
It is evident that essential life processes such as metabolism, translation, splicing, etc. have evolved around RNA even before DNA has evolved as a genetic material.
Structure of Ribonucleotide chain:
In RNA also each nucleotide has three component as in DNA.
- Nitrogenous base –
Purine: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
Pyrimidine – Cytosine (C) and Uracil (U)
- The sugar is Ribose which has an additional -OH group on the second position.
- Phosphate group.
The nucleoside and nucleotide are called ribonucleoside and ribonucleotide respectively.
Types of RNA:
RNA are of three types:
- tRNA (transfer or soluble RNA)
- mRNA (messenger RNA)
- rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
m-RNA: Messenger RNA
- It brings the genetic information of DNA transcribed on it for protein synthesis.
- It is single stranded.
- It is formed on specific part of DNA called structural gene as a complementary copy of one strand of it.
- RNA forms a template for protein synthesis.
t-RNA: Transfer or Soluble RNA
- It act as an adaptor molecule which brings amino acid and read the genetic code.
- tRNA has a clover leaf like secondary structure but actually it is inverted L- shaped compact molecule.
- It has an amino acid acceptor end (3′ end) and anticodon loop where the three bases are complementary to the bases of codon of particular amino acid.
r-RNA: Ribosomal RNA
- It forms the structure of RNA. It is the most abundant RNA.
- It also plays a catalytic role during translation.
Questions & Answers
Question
Why is DNA a better genetic material?
Ans.
DNA rather than RNA carries the hereditary genetic code in all biological life on earth. DNA is both resilient and more easily repaired than RNA. Extra -OH group on second position of carbon of sugar make the RNA more catalytic and unstable. As a result DNA serve as a more stable carrier of genetic information.
Question
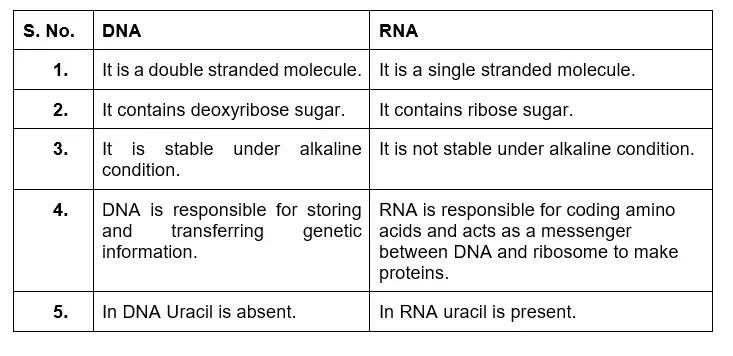
Differentiate between DNA and RNA?
Answer