- Do you know which biomolecule or nutrient is present in rice, potato, banana, bread etc. The answer is ‘Carbohydrates’. In simple words ‘Sugars’ or Hydrates of carbon.
- Carbohydrates are organic molecules that contain carbon Oxygen and hydrogen and are the most abundant organic compounds in nature. They serve as form of energy source, storage and structural components for plants and some animals.
- They have the basic formula (CH2O)n
- Carbohydrates are Aldo keto Sugar.
- It contains two functional group in its structure: An hydroxyl group (-OH), An aldehyde/ketone group
Types of Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are usually divided into the following classes:
- Monosaccharides or simple sugar
- Oligosaccharide
- Polysaccharides
Monosaccharide:
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and the building blocks of the more Complex carbohydrates.
Sugar containing 3-6 carbons atoms are known as monosaccharides. They may exist in a open chain (mostly from 3 to 5 carbon) or in a ring chain configuration (more than 5 carbons).
- Trioses (sugar containing 3 carbon): Glyceraldehyde, Dihydroxyacetone
- Tetroses ( sugar containing 4 carbon): Erythrose
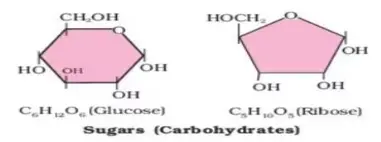
- Pentoses ( sugar containing 5 carbon):Ribose, Arabinose
- Hexose (sugar containing 6 carbon):Glucose, Galactose, Fructose, Mannose
Hexose are divided into aldose (Glucose, Galactose), or ketose (Fructose) sugar according to whether they contain an aldehyde or keto group.
Oligosaccharides:
Oligosaccharides are formed by condensation of 2-10 monosaccharides.
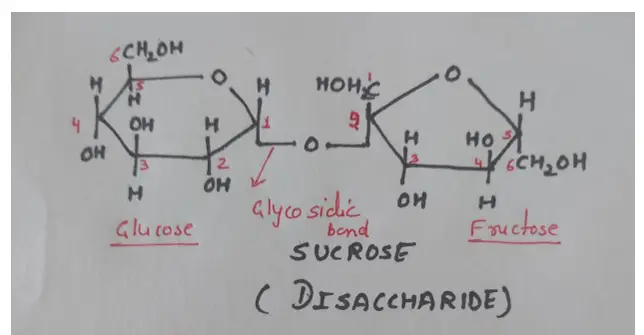
A Disaccharides: oligosaccharide with a combination of two molecules of monosaccharides. When two monosaccharides molecules linked by mean of Alpha 1 – 4 glycosidic bond, a molecule of water is released, a disaccharide molecule is formed. For example; Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose.
B. Trisaccharide: oligosaccharide with a combination of three molecules of monosaccharides. For example; Raffinose.
Polysaccharides:
Polysaccharides are formed by condensation of many monosaccharides.
For example; Cellulose, Starch.
Polysaccharides are of two types:
Homopolysaccharides: Made up of the same kind of monosaccharides.
For example; Cellulose. It is polymer of glucose molecule
Heteropolysaccharides: Made up of different kinds of monosaccharides.
For example; Peptidoglycan. It is made up of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid.
