Activity 10.2: Ncert book Science class 10
In this article, we will discuss Activity 10.2 class 10 science, from Chapter 10 of the NCERT Class 10 Science textbook. The activity demonstrates the behavior of concave mirrors and helps students understand the concept of focal length.
Activity 10.2 Class 10 Science: Exploring Concave Mirrors
Objective
- To understand how concave mirrors reflect and converge light.
Theory
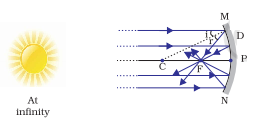
The image you see in a concave mirror is real. When the object is very far away, like the sun, the image formed is focused in the form of a beam. If the mirror is big enough, this focused beam of light can easily burn the paper.
Materials Required
- A concave mirror
- A sheet of paper
- Sunlight
Procedure
- Hold the concave mirror in your hand and direct its reflecting surface towards the Sun.
- Direct the light reflected by the mirror onto a sheet of paper held close to the mirror.
- Move the sheet of paper back and forth gradually until you find a bright, sharp spot of light on the paper.
- Hold the mirror and the paper in the same position for a few minutes.
- Observe what happens to the paper and record your observations.
Observations and Explanation
You will notice that the paper first begins to burn, producing smoke, and may eventually catch fire. This happens because the light from the Sun is converged at a point by the mirror, forming a sharp, bright spot on the sheet of paper. This spot of light is actually the image of the Sun on the paper. The point where the light converges is the focus of the concave mirror.
Understanding Focal Length
Focal length is a crucial parameter that defines the behavior of a mirror. In the case of a concave mirror, the focal length is the distance between the mirror’s surface and the point where parallel rays of light converge after reflection. The focal length can be used to calculate the position and size of the image formed by a concave mirror when an object is placed at a certain distance from it. This concept is an essential part of the study of light, reflection, and refraction.
Conclusion
This activity shows that a real, inverted, point-sized image is formed when a parallel beam of light from an object at infinity (in this case, the sun) hits a concave mirror. The light from the Sun is converged at a point on the paper by the mirror. This point is called the focus of the concave mirror. The heat produced due to the concentration of sunlight ignites the paper. The distance between this image and the position of the mirror gives an approximate value of the focal length of the mirror.
Questions based on this activity
Q1: What type of mirror is used in Activity 10.2 Class 10 Science?
A1: A concave mirror.
Q2: What happens to the paper when sunlight is focused on it using the concave mirror?
A2: The paper begins to burn, producing smoke, and may eventually catch fire.
Q3: What does the bright spot of light on the paper represent?
A3: The image of the Sun formed by the concave mirror.
Q4: At what point on the concave mirror is the light converged?
A4: The focus of the concave mirror.
Q5: What can be approximated using the distance between the image and the mirror?
A5: The focal length of the concave mirror.
