
Activity 2.2 Class 10 science
This Activity 2.2 class 10 science is about exploring olfactory indicators in Acids, Bases, and Salts.
In our day-to-day life, we often come across various substances that change their smell when mixed with an acid or a base. These substances are known as olfactory indicators.
Aim (or Objective)
- In this activity, we will explore the concept of olfactory indicators using common household items such as onions, vanilla essence, and clove oil.
Materials Required
- Finely chopped onions
- Clean cloth strips
- Plastic bag
- Dilute Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) solution
- Dilute Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) solution
- Vanilla essence
- Clove oil
- Test tubes
Explanation
Onion: Odour and Colour
- Onions possess a unique smell due to the presence of a sulphurous compound known as allium. This compound is responsible for the characteristic onion odour.
- Allium, being acidic, reacts with bases such as sodium hydroxide, resulting in an odourless compound. Hence, when a base is added to an onion-soaked cloth, the smell dissipates.
- However, allium does not react with acids. Therefore, the onion odour persists when an acid is added to the onion-soaked cloth.
- Regarding the colour of onions, it remains unaffected by reactions with acids or bases. Thus, the colour of the onion-soaked cloth stays the same irrespective of the addition of acids or bases.
Vanilla: Odour and Colour
- Vanilla has a pleasant smell due to the presence of an aldehyde compound. This compound is also a weak acid.
- When a base is added to vanilla, the aldehyde reacts with it, causing the pleasant vanilla smell to disappear.
- Similar to onions, the colour of vanilla is not influenced by reactions with acids or bases. Therefore, the colour of vanilla remains constant, regardless of whether an acid or a base is added.
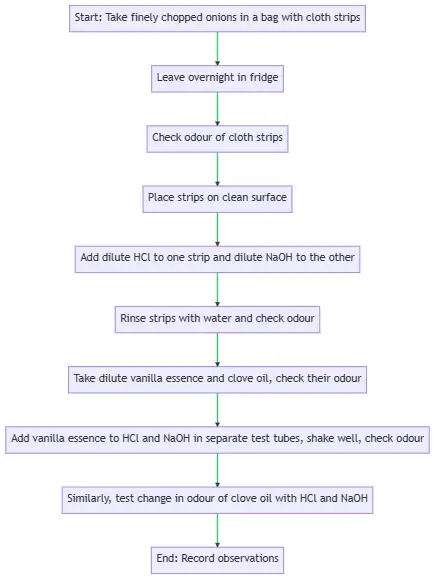
Procedure
Preparation of Onion Strips
- Place finely chopped onions and clean cloth strips in a plastic bag.
- Securely tie the bag and leave it in the fridge overnight.
- The cloth strips, now soaked in onion juice, are ready for testing with acids and bases.
Testing with Acid and Base
- Take two onion-soaked cloth strips and note their initial odour.
- Place a few drops of dilute HCl solution on one strip and dilute NaOH solution on the other.
- Rinse both strips with water and check their odour again.
- Record any changes in the odour of the strips.
Testing with Vanilla Essence and Clove Oil
- Check the odour of dilute vanilla essence and clove oil.
- Add a few drops of each to separate test tubes containing dilute HCl and NaOH solutions.
- Shake the test tubes well and check the odour again.
- Record any changes in the odour of the solutions.
Conclusion
Based on the observations, determine which substances – vanilla, onion, or clove – can be used as olfactory indicators.
Application
- Onions are often seen immersed in a red-coloured solution, particularly in homes and restaurants. This solution is typically potassium permanganate.
- Potassium permanganate is a mildly basic salt. When onions are soaked in this solution, it neutralizes the sulphurous allium compound in the onions, effectively eliminating the pungent onion smell.
- In addition to deodorizing the onions, potassium permanganate also acts as a preservative. This helps in extending the shelf life of onions, allowing them to be stored for longer periods without spoiling.
Questions based on Activity 2.2 Class 10 Science
Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the compound present in onions that gives them their distinctive smell?
a) Vanillin
b) Potassium permanganate
c) Allium
d) Sodium hydroxide - What happens when a base is added to an onion-soaked cloth?
a) The smell of the onion intensifies
b) The smell of the onion disappears
c) The colour of the onion changes
d) Nothing happens - What is the compound present in vanilla that gives it its pleasant smell?
a) Allium
b) Aldehyde
c) Sodium hydroxide
d) Potassium permanganate - What happens to the colour of onions and vanilla when they react with acids or bases?
a) The colour changes to red
b) The colour changes to blue
c) The colour remains the same
d) The colour disappears - What is the purpose of soaking onions in a potassium permanganate solution?
a) To change the colour of the onions
b) To make the onions taste better
c) To deodorize and preserve the onions
d) To make the onions smell stronger
Answers
- Answer: c) Allium
- Answer: b) The smell of the onion disappears
- Answer: b) Aldehyde
- Answer: c) The colour remains the same
- Answer: c) To deodorize and preserve the onions Conceptual Questions
Questions and Answers
Question: What is an olfactory indicator and how does it work?
Answer: An olfactory indicator is a substance that changes its smell when mixed with an acid or a base. It works by reacting with the acid or base, resulting in a chemical change that alters its odour.
Question: Why does the smell of an onion-soaked cloth disappear when a base is added?
Answer: The smell of an onion-soaked cloth disappears when a base is added because the sulphurous allium compound in the onion, which is acidic, reacts with the base to form an odourless compound.
Question: Why does the pleasant smell of vanilla disappear when a base is added?
Answer: The pleasant smell of vanilla disappears when a base is added because the aldehyde compound in vanilla, which is a weak acid, reacts with the base, causing the smell to disappear.
Question: Why does the colour of onions and vanilla remain the same when they react with acids or bases?
Answer: The colour of onions and vanilla remains the same when they react with acids or bases because their colour is not influenced by these reactions. The colour of a substance is determined by the wavelengths of light it absorbs, which is not affected by the presence of acids or bases.
Question: How does potassium permanganate help in preserving onions?
Answer: Potassium permanganate helps in preserving onions by acting as a preservative. When onions are soaked in a potassium permanganate solution, it neutralizes the sulphurous allium compound in the onions, effectively eliminating the pungent onion smell. This helps in extending the shelf life of onions, allowing them to be stored for longer periods without spoiling.