
Activity 2.1 in Class 10 Science NCERT Book
Activity 2.1 from the NCERT Class 10 Science textbook, chapter 2, “Acids, Bases, and Salts”, provides an engaging way to experience the reactions between different solutions and chemical indicators. This activity helps students understand the behavior of acids and bases and sets the foundation for understanding the concepts of pH, neutralization, and titration.
Aim (or Objective) Of activity 2.1
Activity 2.1 requires us to test various acids and bases with different reagents one at a time and observe the results.
Materials Used
The acids and bases tested in this activity include
- hydrochloric acid $(HCl)$,
- sulphuric acid $(H_2SO_4)$,
- nitric acid $(HNO_3)$,
- acetic acid $(CH_3COOH)$,
- sodium hydroxide $(NaOH)$,
- calcium hydroxide $[Ca(OH)_2]$,
- potassium hydroxide $(KOH)$,
- magnesium hydroxide $[Mg(OH)_2]$, and
- ammonium hydroxide $(NH_4OH)$
Indicators
The indicators used in this activity are
- Blue litmus paper: A naturally occurring indicator that turns red in acidic solutions and blue in basic solutions.
- Red litmus paper: A naturally occurring indicator that turns blue in basic solutions and red in acidic solutions.
- Phenolphthalein: An organic indicator that turns colorless in acidic solutions and pink in basic solutions.
- Methyl orange: An organic indicator that turns red in acidic solutions and yellow in basic solutions.
These indicators change color when they come into contact with an acid or a base.
Procedure
- Collection of Materials: Collect the following solutions from the science laboratory: hydrochloric acid $(HCl)$, sulphuric acid $(H_2SO_4)$, nitric acid $(HNO_3)$, acetic acid $(CH_3COOH)$, sodium hydroxide $(NaOH)$, calcium hydroxide $[Ca(OH)_2]$, potassium hydroxide (KOH), magnesium hydroxide $[Mg(OH)_2]$, and ammonium hydroxide $(NH_4OH)$.
- Preparation for Testing: Place a drop of each of the above solutions on a separate watch glass.
- Testing with Indicators: Test each solution with a drop of the following indicators: red litmus, blue litmus, phenolphthalein, and methyl orange.
- For litmus tests, dip a piece of the appropriate litmus paper into the solution and observe the color change.
- For phenolphthalein and methyl orange, add a few drops of the indicator to the solution and observe the color change.
- Recording Observations: Record the color changes for each solution with each indicator in a table for comparison and analysis.
Remember to handle all chemicals with care and under the supervision of a teacher or an experienced adult.
Observations for activity 2.1 Class 10 science
- Strong acids like hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, and nitric acid turn blue litmus red and give a red solution with methyl orange.
- Strong bases like sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, and ammonium hydroxide turn red litmus blue. They also give a pink solution with phenolphthalein and a yellow solution with methyl orange.
The table given below showcases the observed color changes when the given solutions interact with each indicator. Please note that this table is based on the typical reactions of these substances. Actual observations may slightly vary depending on the exact concentration of the solutions and indicators.
Observation Table for activity 2.1 Class 10 science
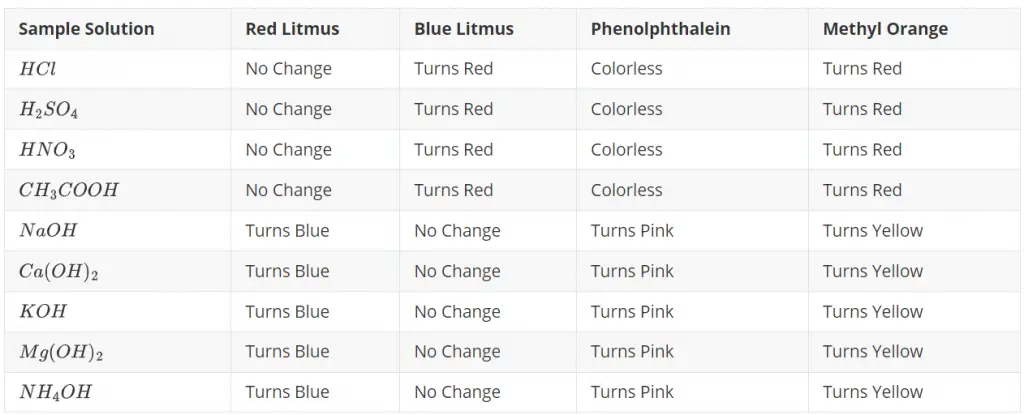
This table shows the inherent property of acids and bases: acids turn blue litmus red and bases turn red litmus blue. Furthermore, the transition of phenolphthalein from colorless in acid to pink in base, and methyl orange from red in acid to yellow in base, gives us another way to differentiate between these two types of substances.
It illustrates how different pH indicators give different colors with acids and bases, thereby helping us identify whether a substance is acidic or basic.
Activity-based question for Activity 2.1 Class 10 Science
Here are some activity-based questions based on this class 10 science NCERT book chapter 2 concepts.
Conceptual Questions
Question 1: What are the characteristic color changes that occur when acids and bases come into contact with blue and red litmus paper?
Answer 1: Acids turn blue litmus paper red, while bases turn red litmus paper blue.
Question 2: How does phenolphthalein react differently when added to an acidic solution versus a basic solution?
Answer 2: Phenolphthalein remains colorless in an acidic solution, while it turns pink or magenta in a basic solution.
Question 3: What is the color change observed when methyl orange is added to a solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH)?
Answer 3: When methyl orange is added to a solution of sodium hydroxide, a base, it turns yellow.
Question 4: Why does the reaction of hydrochloric acid (HCl) with blue litmus result in a color change, while the reaction of HCl with red litmus does not?
Answer 4: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is an acid, and it turns blue litmus paper red. Red litmus paper does not change color when it comes in contact with an acid; hence, no color change is observed.
Question 5: If an unknown solution turns blue litmus paper red, phenolphthalein colorless, and methyl orange-red, what can you infer about the solution?
Answer 5: The solution is likely to be an acid, as these are the characteristic reactions of acids with these indicators.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1: Which of the following is true about the reaction of acids with blue litmus paper?
a) They turn it red.
b) They turn it blue.
c) They turn it green.
d) No color change occurs.
Answer 1: a) They turn it red.
Explanation: Acids have the property of turning blue litmus paper red.
Question 2: Phenolphthalein in an acidic solution turns:
a) Pink
b) Yellow
c) Colorless
d) Blue
Answer 2: c) Colorless
Explanation: Phenolphthalein remains colorless in acidic solutions, while it turns pink in basic solutions.
Question 3: When methyl orange is added to a solution of sodium hydroxide $(NaOH)$, it will turn:
a) Red
b) Yellow
c) Pink
d) Colorless
Answer 3: b) Yellow
Explanation: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a base, and when methyl orange is added to it, the solution turns yellow. This is a characteristic behavior of bases with the methyl orange indicator.
Question 4: If an unknown solution turns blue litmus paper red and phenolphthalein colorless, it is likely to be:
a) A base
b) An acid
c) A salt
d) Water
Answer 4: b) An acid
Explanation: The characteristic property of acids is to turn blue litmus paper red, and phenolphthalein remains colorless when added to an acid. Hence, the unknown solution is likely an acid.
Question 5: Red litmus paper will turn blue in the presence of:
a) Hydrochloric acid $(HCl)$
b) Acetic acid $(CH_3COOH)
c) Sodium hydroxide $(NaOH)$
d) Nitric acid $(HNO_3)$
Answer 5: c) Sodium hydroxide $(NaOH)$
Explanation: Bases turn red litmus paper blue. Sodium hydroxide $(NaOH)$ is a base, so it will cause this color change. Acids like Hydrochloric acid $(HCl)$, Acetic acid $(CH_3COOH)$, and Nitric acid $(HNO_3)$ do not change the color of red litmus paper.
