In this article, we’ll talk about the dimensions of pressure. Here, we will look at the dimensional formula of pressure and how to find the dimensions of pressure.
Pressure is defined as the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. $\frac{F}{A}$ is the basic pressure formula (Force per unit area). Pascals is the SI unit of pressure (Pa). In SI base units 1 $N/m^2$, $1 kg/(m·s^2)$, or $1 J/m^3$ are the units of pressure.
Increasing the amount of force applied to any object increases the amount of pressure applied. As a result, the greater the force, the greater the pressure applied. This effect occurs because, according to our definition, pressure varies directly with force $\left (\frac{F}{A}\right )$. By reducing the area over which the force acts, you can increase the pressure caused by the same force.
Dimensional Formula of Pressure
Dimensional Formula for Pressure is given by
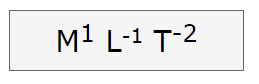
Here
M denotes Mass
L denotes Length
T denotes Time
Derivation for dimensions of pressure
Pressure is defined as Force per unit area
$Pressure = \frac {Force}{Area}$
Now
Force is defined as
$F= ma$
Dimension of Mass is $[M^1L^0T^0]$
Dimension of acceleration is $[M^0L^1T^{-2}]$
So the dimension of Force will be
$=[M^1L^0T^0] \times [M^0L^1T^{-2}] = [M^1L^1T^{-2}]$
Now Dimension of Area = $[M^0L^2T^0]$
Substituting these values of dimension of Force and area, we get the dimensional formula of Pressure as
$\text {dimensional formula of Pressure} = \frac { [M^1L^1T^{-2}]}{[M^0L^2T^0]} = [M^1L^{-1}T^{-2}]$
Pressure is denoted by Letter $P$
SI unit of pressure is Pascal or Newton/square meter
Try the free Quiz given below to check your knowledge of Dimension Analysis:-
Quiz on Dimensional Analysis
Other Dimensional Formulas
| Dimension of Surface Tension | Dimension of Impulse |
| Dimension of Momentum | Dimensional Formula of Spring constant |
Apart from these check out the Dimensional Analysis page on hyperphysics website along with other excellent resources.
