Exploring Reactions of Metals with Acids and Bases: Activity 2.4
Introduction
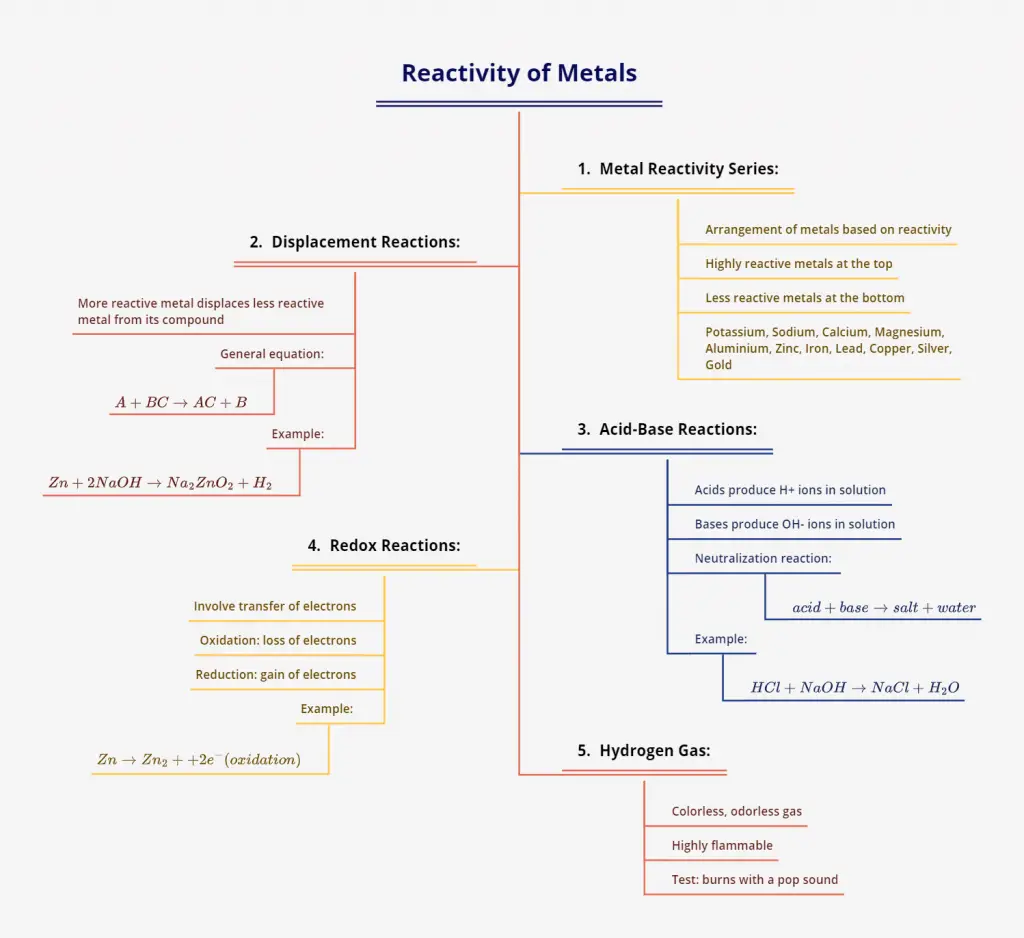
This activity, part of the Class 10 NCERT Science chapter on Acids, Bases, and Salts, explores the reactions of metals with acids and bases. Students will observe the formation of hydrogen gas and learn about the displacement reactions that occur.

Materials Needed
- Granulated zinc metal
- Sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH)
- Test tube
- Bunsen burner or spirit lamp
- Lime water (Ca(OH)?)
- Delivery tube
- Beaker
Procedure
- Place a few pieces of granulated zinc metal in a test tube.
- Add 2 mL of sodium hydroxide solution to the test tube.
- Warm the contents of the test tube using a Bunsen burner or spirit lamp.
- Collect the gas produced in another test tube by displacement of water.
- Test the collected gas with a burning splint.
- Pass the gas through lime water in a separate beaker.
Observations
- Bubbles are observed in the test tube containing zinc and sodium hydroxide.
- A colorless, odorless gas is collected in the second test tube.
- The collected gas burns with a pop sound when a burning splint is brought near it.
- The lime water remains clear when the gas is passed through it.
Explanation of Chemical Reactions
The reaction between zinc and sodium hydroxide can be represented by the following equation:
$$2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) \rightarrow Na_2ZnO_2(s) + H_2(g)$$
In this reaction, zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium zincate $(Na_2ZnO_2)$ and hydrogen gas $(H_2)$. This is an example of a metal reacting with a base to produce hydrogen gas.
It’s important to note that not all metals react with bases in this way. The reactivity of metals varies, and some metals may not react with bases at all.
Conclusion
This activity demonstrates that certain metals, like zinc, can react with bases such as sodium hydroxide to produce hydrogen gas. This reaction is different from the reaction of metals with acids, which we explored in previous activities. Understanding these reactions helps us comprehend the chemical behavior of metals in different environments.
Questions and Answers
- Q: Why does zinc react with sodium hydroxide?
A: Zinc is a reactive metal that can displace hydrogen from bases like sodium hydroxide. - Q: What is the name of the compound formed when zinc reacts with sodium hydroxide?
A: Sodium zincate $(Na_2ZnO_2)$ - Q: How can you identify that the gas produced is hydrogen?
A: The gas burns with a pop sound when a burning splint is brought near it, which is characteristic of hydrogen. - Q: Why doesn’t the lime water change when the gas is passed through it?
A: The gas produced is hydrogen, which doesn’t react with lime water. Only carbon dioxide causes lime water to turn milky. - Q: Can this reaction occur with all metals?
A: No, not all metals react with bases in this way. The reactivity depends on the specific metal and its position in the reactivity series.
Safety Precautions
- Handle sodium hydroxide solution with care as it is corrosive.
- Wear safety goggles and gloves during the experiment.
- Use caution when heating the test tube and handling the Bunsen burner.
- Perform the experiment in a well-ventilated area.
Mind map: Reactivity of Metals