

As per the question,time period depends on Pressure,density and energy
$T=C P^a \rho ^b E^c$ where, symbols have their usual meaning and C is a constant
Now we need to find the values of a,b,c by using dimensional analysis
Expressing in terms of dimensions,
$[T] = [ML^{-1}T^{-2}]^a[ML^{-3}]^b[ML^2T^{-2}]^c$
Comparing the exponents of M,T and L, we get three equation in a,b,c
0 = a+b+c
1 = -2a-2c
0 = -a-3b+2c
Solving these linear equation in three variable,we get
a= -5/6 , b= 1/2 ,c=1/3
Hence,
$T = C \frac {\rho ^{\frac {1}{2}} E^{\frac {1}{3}}}{P^{\frac {5}{6}}}$
The magnitudes of physical quantities can be added together or subtracted from one another only if they have the same dimensions. So, the dimensions of d will be [T]
Now Velocity has the dimension $[LT^{-1}]$, Now each of the quantity which are being added on the RHS should also have same dimension
so bt should also have $[LT^{-1}]$ dimension, which means b dimension is $[LT^{-2}]$
Now $\frac {c}{d+t}$ should also $[LT^{-1}]$ dimension, which means c dimension is $[L]$
Now $\sqrt {ab}$ should have $[LT^{-1}]$ dimension,which means a dimension is [L]
So a represent length, b represent acceleration, c represent length and d represent time
Given that, \(M=2\times 10^{30}kg\,\, R=7\times 10^8m\)
Lets calculate the density based on the given data
\begin{align*}
Density, \,\, \rho \,\,&=\frac{mass}{volume}=\frac{M}{\frac{4}{3}\pi R^3}\\
&=\frac{3M}{4\pi R^3}\\
&=\frac{3\times 2\times 10^{30}}{4\times 3.14\times \left( 7\times 10^8 \right) ^3}\\
&=\text{1.392 }\times 10^3kg/m^3
\end{align*}
Which is the order of density of solids and liquids not gases.High density of sun is because of inward gravitational attractions or the outer layers of the sun.
Error in X is given by
$\frac {\Delta X}{X}= \frac {\Delta a}{a} + 2 \frac {\Delta b}{b} + \frac {\Delta c}{c} $
$\frac {\Delta X}{X} =\frac {4}{100} + 2 \frac {2}{100} + \frac {3}{100} $
$\frac {\Delta X}{X} =\frac {11}{100} $
So percentage error is X is 11%
Volume is given by
$V= \pi r^2 H$
Error in V is given by
$ \frac {\Delta V}{V} = 2\frac {\Delta r}{r} + \frac {\Delta h}{h}$
$ \frac {\Delta V}{V} = 2\frac {x}{100} + \frac {y}{100}$
$ \frac {\Delta V}{V} = \frac {2x + y}{100}$
So ,percentage error is (2x+y)
A.U stands for Astronomical unit. 1 A.U =$1.496 \times 10^{11} m$
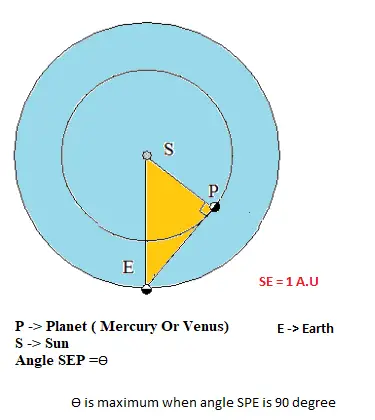
Some Theory around the question. This question is based on Copernicus method.Some point to remember
a. The planets which are closer to the Sun than the Earth are called inferior planets.
b.The Mercury and the Venus are two inferior planets.
c. Copernicus assumed the orbits of inferior planets as perfectly circular.
d. The angle formed at the Earth between the Earth planet direction and the Earth-Sun Direction is called the planet elongation and is denoted by symbol $\theta$
e. The planets elongation changes continuously as planets are moving.
f. When elongation acquires maximum value it appears to be farthest from the sun, At this time the Sun and the Earth subtends an angle of 90° at the planet.
g. Average Distance between Sun and earth is 1 A.U
unit-and-dimension-question-1.png
Now applying Pythagoras Theorem
$SE^2 =SP^2 + PE^2$
$1 = (.38)^2 + PE^2$
$PE^2 = .8556$
PE=.924 A.U
Lets first calculate the light year
Now we know that distance travelled by light in 1 year is called 1 light year
Speed of light = $ 3 \times 10^8$ m/s and $1 year =365 \times 24 \times 60 \times 60$ s
So 1 light year = $3 \times 10^8 \times 365 \times 24 \times 60 \times 60 $ m
\( 1light\,\,year=9.46\times 10^{15}m\)
\begin{align*}
x=4.29\,light\,\,year &=4.29\times 9.46\times 10^{15}m\\
&=\frac{4.29\times 9.46\times 10^{15}}{3.08\times 10^{16}}par\sec =1.323 parsec
\end{align*}
In an orbit around the sun, the distance between six months apart locations is diameter of the Earth orbit itself which is $3 \times 10^{11}m$.
Now, using parallax method
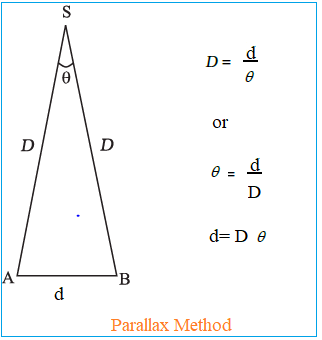
\begin{align*}
\therefore \theta =\frac{d}{D}&=\frac{3 \times 10^{11}}{x}=\frac{3 \times 10^{11}}{4.29\times 9.46\times 10^{15}}rad\\
&=1.512\,sec
\end{align*}
The density of the block is given by
$ \rho = \frac {mass}{volume} =\frac {m}{L \times b \times t}$
Calculating with giving values
$\rho= \frac {39.39}{ 5.12 \times 2.56 \times 0.37} = 8.1037$ g/cm3
Now uncertainty given in various quantities as per the given Least count of the instruments
$m = \pm 0.01$g
$l = \pm 0.01$ cm
$b = \pm 0.01$ cm
$t = \pm 0.01$ cm
Maximum relative error, in the density value is, therefore, given by
$ \frac {\Delta \rho}{\ rho} = \frac {\Delta m}{m} + \frac {\Delta L}{L} + \frac {\Delta b}{b} + \frac {\Delta t}{t}$
$= \frac {0.1}{39.3}+ \frac {0.01}{ 5.12} + \frac {0.01}{2.56} + \frac {0.01}{0.37} $
$= 0.0019 + 0.0039 + 0.027 + 0.0024= 0.0358$
Hence $ \Delta \rho= 0.0358 \times 8.10379 = 0.3$ g/cm3
We cannot, therefore, report the calculated value of $\rho$ (= 8.1037 g/cm3) up to the fourth decimal place. Since $\Delta \rho = 0.3$g/cm3 the value of density can be regarded as accurate up to the first decimal place only. Hence the value of density must be rounded off as 8.1 g/cm3 and the result of measurements should be reported as
$\rho = (8.1 \pm 0.3)$ g/cm3
Volume of the rectangular block(V) is given by
V=LBH
Now L=1.37 cm,B=4.11 cm,H=2.56 cm
$V=4.11 \times 2.56 \times 1.37=14.41$ cm3
For Vernier callipers,Least count is 0.01 cm.
If all your measurements were 0.01 cm lower, the volume would be
$V=4.10 \times 2.55 \times 1.36=14.21$ cm3
If all your measurements were 0.01 cm higher, the volume would be
$V=4.12 \times 2.57 \times 1.37=14.61$ cm3
We can see the maximum value is .20 higher then calculated values
So we could report answer as $(14.41 \pm 0.20)$ cm3
Given Cp=(12.28±0.2) units and CV=(3.97±0.3) units.
$R=C_P-C_V = (12.28\pm 0.2) - (3.97\pm 0.3) = (8.31 \pm 0.5)$ units

The magnitude of the difference between the individual measurement and the true value of the quantity is called the absolute error of the measurement
The accuracy of a measurement is a measure of how close the measured value is to the true value of the quantity.
Precision tells us to what resolution or limit the quantity is measured.
The relative error is the ratio of the mean absolute error $\Delta a_{mean}$ to the mean value $a_{mean}$ of the quantity measured.
$a_{mean} = \frac {a_1 + a_2 + a_3}{3}$
$\Delta a_{mean}= \frac {|a_1 - a_{mean}| + |a_2 - a_{mean}| + |a_3 - a_{mean}|}{3}$
Parallax error occurs when the measurement of an object's length is more or less than the true length because of your eye being positioned at an angle to the measurement markings