Exploring Acid-Base Neutralization: Activity 2.6 from Class 10 NCERT Science
Introduction
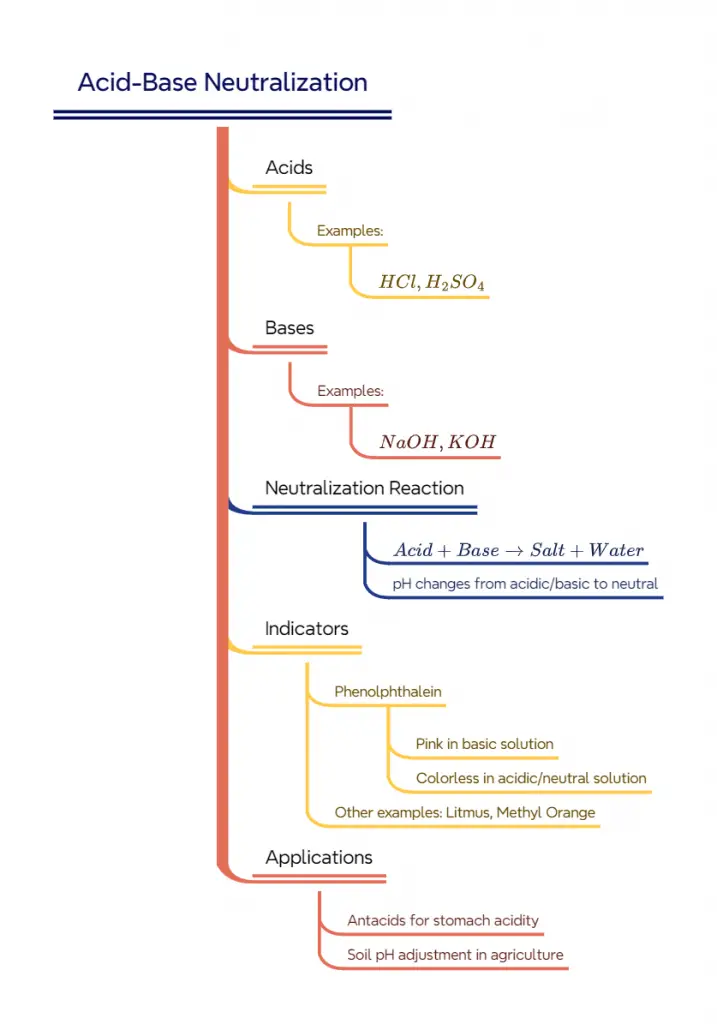
Activity 2.6 from the Class 10 NCERT Science book explores the fascinating world of acid-base reactions and neutralization. This activity, part of the chapter on Acids, Bases, and Salts, demonstrates how acids and bases interact and how indicators can be used to observe these reactions.

Materials Needed
- Dilute sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution
- Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution
- Phenolphthalein indicator solution
- Test tube
- Dropper
Procedure
- Take about 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube.
- Add two drops of phenolphthalein solution to the NaOH.
- Observe the color of the solution.
- Add dilute HCl solution to the above solution drop by drop.
- Observe any color changes in the reaction mixture.
- Add a few drops of NaOH to the mixture.
- Observe if the pink color reappears.
Observations
- When phenolphthalein is added to NaOH, the solution turns pink.
- As HCl is added drop by drop, the pink color gradually fades and eventually becomes colorless.
- When NaOH is added again, the pink color reappears.
Explanation
This activity demonstrates the concept of acid-base neutralization and the use of indicators. Here’s what’s happening:
- Phenolphthalein is an indicator that turns pink in basic solutions (pH > 8.2) and remains colorless in acidic or neutral solutions.
- The initial pink color is due to the basic nature of NaOH: ${NaOH(aq) \rightarrow Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)}$
- When HCl is added, it neutralizes the NaOH: ${NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) \rightarrow NaCl(aq) + H_2O(l)}$
- As the solution becomes neutral, phenolphthalein turns colorless.
- Adding NaOH again makes the solution basic, causing the pink color to reappear.
The general neutralization reaction can be written as:
${Base + Acid \rightarrow Salt + Water}$
Conclusion
This activity demonstrates how acids and bases interact to form salt and water, a process known as neutralization. It also shows how indicators like phenolphthalein can be used to visually observe changes in pH during chemical reactions.
Questions and Answers
- Q: Why does phenolphthalein turn pink in NaOH solution?
A: Phenolphthalein turns pink in basic solutions (pH > 8.2), and NaOH is a strong base. - Q: What happens when HCl is added to the pink NaOH-phenolphthalein solution?
A: The pink color gradually fades as HCl neutralizes the NaOH, eventually becoming colorless. - Q: Write the balanced equation for the neutralization reaction between NaOH and HCl.
A: ${NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) \rightarrow NaCl(aq) + H_2O(l)}$ - Q: Why does the pink color reappear when more NaOH is added after neutralization?
A: Adding more NaOH makes the solution basic again, causing phenolphthalein to turn pink. - Q: What is the product of an acid-base neutralization reaction?
A: The products are always a salt and water.
Safety Precautions
- Handle acids and bases with care, as they can be corrosive.
- Wear safety goggles and gloves when performing this activity.
- In case of skin contact with acids or bases, rinse immediately with plenty of water.
Concept Mind Map – Acid-Base Neutralization