

All Living things produce more of their own kind The process through which a living thing (organism) produces new living things (young ones) like itself is called reproduction.
Reproduction in plants occurs in two ways:
Fragmentation, budding, spore formation and vegetative propagation are some of the different type of asexual reproduction.
In this method the body of parent organism breaks into 'fragments' and each fragment can grow to function as a new individual. For example; Algae like Oscillatoria and Spirogyra are reproduced by fragmentation.
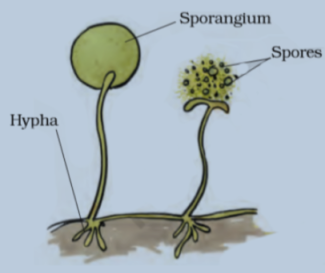
Spores are tiny, spherical unicellular bodies protected by a thick wall to withstand to unfavorable conditions When the conditions are favorable, these spores germinate into new individuals. Mosses, ferns, fungi, etc. reproduce by this method.
In some plants, any vegetative part of a plant such as the root, stem or leaf can give rise to new plant. This type of asexual reproduction is called vegetative propagation. Vegetative propagation can take place naturally and can also be carried out by artificial means.
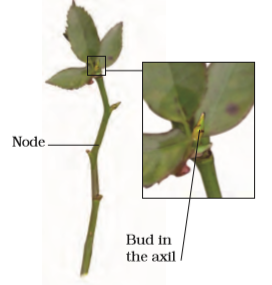
From stem: New plants can grow either from horizontal stem or from underground stem.
From Horizontal stems:
| Runner | Slender branch that creeps some distance away from the mother plant on the ground, root itself at the nodes and grows into a new plant. Ex. Wood sorrel and grass. |
| Stolons | that arise from the base of the stem, root at the nodes, producing buds that soon grow into daughter plants. Ex. White, strawberry and peppermint |
| Offset | Water lettuce |
| Suckers | Chrysanthemum |
Underground stem
| Bulbs | Bulbs are underground stems with thick fleshy scaly leaves that store food around the bud. Ex. Onion Garlic, Lily and Tulip. |
| Rhizome | Rhizomes are underground stems that have scaly leaves at their nodes. The axil of the scaly leaf has buds that grow into new shoots upward. Ex. Ginger asparagus and water lily. |
| Tubers | Potato is a modified stem and has buds. It is called a tuber. When a piece of potato containing a bud is planted into the soil, it can grow into a new potato plant. |

Some plants like sweet potato and dahlia have swollen roots without any shape. These roots are called tuberous roots. These roots have small buds which give rise to a new plant when they are planted into the soil.
Plants like Bryophyllum produce buds from the margin of the leaves. These buds drop off from the leaves and fix themselves to the ground and later grow into new plants.
In this method, the growing tips of plants are cut and planted in an artificial medium kept inside a conical flask or a test tube. The medium provides all the necessary nutrients and plant hormones for plant growth. Once the roots develop, they are planted in suitable soil. From here, they grow into whole new plants.
In sexual reproduction, in male cell (gamete) produced by the male part of the flower fuses with female cell (gamete) produced by the female part of the flower. The fusion of the male and female gametes known as fertilization, leads to the formation of single cell called the zygote. This cell divides and redivides and slowly give rise to a new individual.
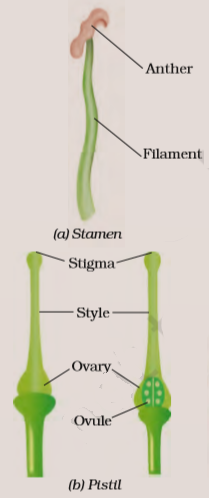
Picture of a typical flower: Flower is the reproductive part of flowering plant. A typical flower has four parts- sepals, petals, stamens and a carpel.
Flowers are of two types:
| Unisexual flowers | Bisexual flowers |
|---|---|
| Flowers with only the male or the female reproductive part are called unisexual flower. They are also called incomplete flowers. | Flowers having both stamens and pistils are called bisexual flowers. They are also called complete flowers. |
| For example: Watermelon, cucumber, papaya | For example: hibiscus, wild rose. |
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same kind of flower is called pollination. Pollination is of two types:
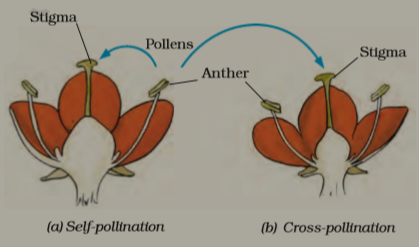
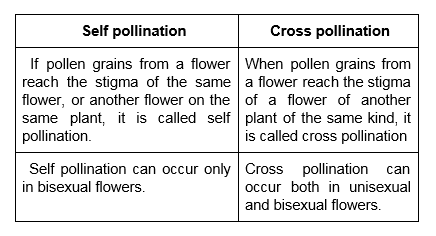
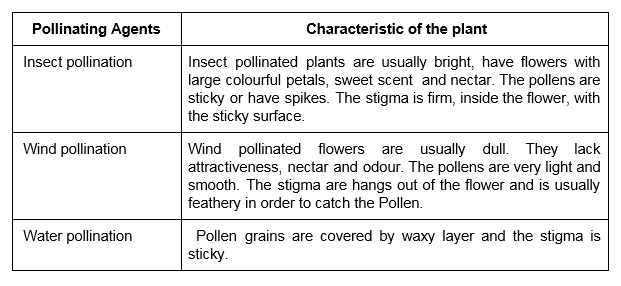
When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of a flower of the same kind, it develops a long tube called Pollen tube. The Pollen tube grows downwards through the style towards the ovary. The male gametes are inside the pollen tube. Once inside the ovary, it enters the ovule. The male gamete fuses with the female gamete and form zygote. The process of fusion of the male and female gamete is known as fertilization. The fertilized cell is known as the zygote. The ovule develops into a seed and the ovary into the fruit after fertilization.
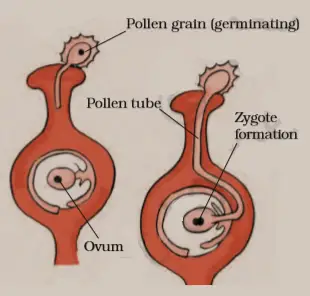
The fertilized egg begins to divide inside the ovule and develops into an embryo. The ovule develops into a seed. The embryo has a radical and plumule. It is attached to one or two cotyledons. Upon germination the radicle will develop into the root system, while the plumule will develop into the shoot system. The cotyledon have a store of food which is used by the seedling.
Once the seeds dry, they get dispersed. Seed dispersal in the scattering of seeds over a large area by various means. The different means of seed dispersal are wind, water,animals and explosion of fruits. Different means of seed dispersal help the plants as it helps the seeds to reach a suitable medium for germination, far away from the parent plant.
Some plants like drumsticks and maple have winged seeds, which are carried by the wind. The seeds of other plants, like milkweed silk cotton and Devil's tree have tufts of hair which help them ride on the wind.
Seeds that are dispersed by water have a spongy coat or a layer of fiber that make them light. This property help them to float on water. The flowing water then carries them too far off places for example coconut.
Birds, monkeys and other animals eat the fruit of many plants and throw away the seeds. Some plants have fruit or seeds with hooks, bristles, or spines. These get attached to the fur of animals or to our clothes. They are carried a long way before they fall off or are brushed off. By exploding fruits: The fruits of the rubber tree, balsam, lady finger, and night jasmine explode when they ripen. The sudden bursting of the fruit scatter the seeds away from the parent plant.
Also Read