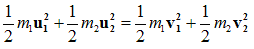 (2)
(2)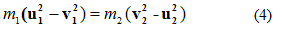
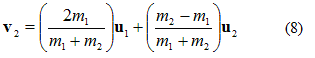
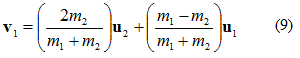
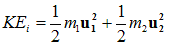
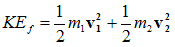
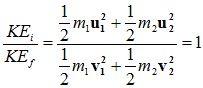
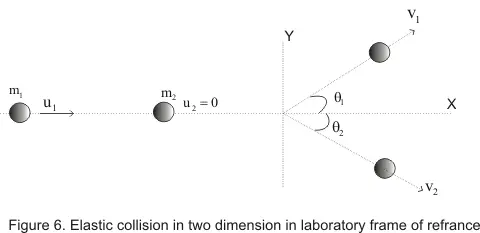
Case II: when the target particle is at rest i,e u2=0
From equation (8) and (9)
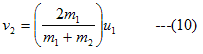
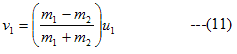
Hence some part of the KE which is transformed into second particle would be
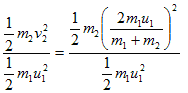
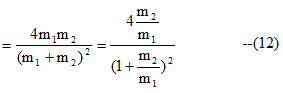
Therefore after collisom first particle moving with initial velocity u1 would come to rest and the second particle which was at rest would start moving with the velocity of first particle.Hence in this case when m1=m2 transfer of energy is 100%.if m1 > m2 or
m1 < m2 ,then energy transformation is not 100%
Therefore when a heavy particle collide with a very light particle at rest ,then the heavy particle keeps on moving with the same velocity and the light particle come in motion with a velocity double that of heavy particle