

Given g=10 m/sec2 and Young Modulus of the material of the wire=2X1011 N/m2
Stress =Load/Area
$=\frac {mg}{A}=\frac {100 \times 10}{10^{-4}} =10^7 \ N/m^2$
Now
Young Modulus=Stress/Strain
So strain= Stress/Young Modulus
$=5 \times 10^{-5}$
Now we know that
Strain = Increase in length/Initial length
=> Increase in Length=strain * Initial length
$=5 \times 10^{-5}$ m
Elastic Potential energy
$ =\frac{1}{2}stress \times strain \times Volume$
$=5 \times 10^{-2} \ J$
The tensions in the load position will the weight of the mass
So T=mg
=100*10=1000 N
Let us consider a small element dx at a distance x from the rotating end.
Now mass of the rod =$L\pi r^2\rho$
Mass per unit length of the rod=$\pi r^2\rho$
Mass of the small element=$\pi r^2dx\rho$
Centripetal force acting on the element
$dF=\pi r^2\rho x\omega^2dx$
The Tension in the element would be due to the centripetal force of the outer portion i.e from x=x to x=L
$F=\int_{x}^{L}{\pi r^2\rho x\omega^2dx}$
$F=\frac{1}{2}\pi r^2\rho\omega^2(L^2-x^2)$
Tension at fixed point
x=0
$F=\frac{\rho\pi r^2\omega^2L^2}{2}$
At x=L/2
$F=\frac{3\rho\pi r^2\omega^2L}{8}$
So tension is maximum at fixed end and decrease towards outer end.
So
$S\pi r^2>\frac{\rho\pi r^2\omega^2L^2}{2}$
Or $\sqrt{\frac{2S}{\rho L^2}}<\omega$
Let dy be the elongation at the element of length dx
Then
$\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{Y}\frac{F(x)}{A}$
Substituting the value of F(x) from previous part
$dy=\frac{\pi r^2\rho\omega^2(L^2-x^2)dx}{2Y\pi r^2}$
$y=\int_{0}^{L}{\frac{\rho\omega^2}{2Y}(L^2-x^2)dx=\frac{\rho\omega^2L^3}{3Y}}$

Let $l_2$ be the elongation in second case then
$T_1=2\pi\sqrt{\frac{l_1}{g}}$ ---(1)
$T_2=2\pi\sqrt{\frac{l_2}{g}}$ ---(2)
So that
$\frac{T_1^2}{T_2^2}=\frac{l_1}{l_2}$
Or
$\frac{l_1}{l_2}=\frac{16}{25}$
Now
For first case
$Y=\frac{MgL}{Al_1} $ --(3)
Second case
$Y=\frac{(M+m)gL}{Al_2}$ --(4)
From 3 and 4
$\frac{l_1}{l_2}=\frac{M}{M+m}$
Or
$\frac{M}{M+m}=\frac{16}{25}$
$\frac{M+m}{M}=\frac{25}{16}$
Or
$\frac{M+m-M}{M}=\frac{25-16}{19}$
Or
$\frac{m}{M}=\frac{9}{16}$
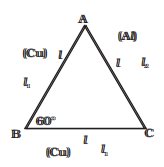
Let $l_1$ = AB, $l_2$ = AC, $l_3$ = BC
$cos \theta = \frac {l_3^2 + l_1^2 -l_2^2}{2l_3L_1}$
or
$2l_3L_1 cos \theta=l_3^2 + l_1^2 -l_2^2$
Differentiating
$2(l_3dL_1 + l_1dl_3 ) cos \theta - 2l_3L_1 sin \theta d\theta=2l_3dl_3 + 2l_1dl_1 - 2l_2dl_2$
Now
$dl_1 = l_1 \alpha _1 \Delta T$
$dl_2 = l_2 \alpha _1 \Delta T$
$dl_3 = l_3 \alpha _2 \Delta T$
and $l_1 = l_2 =l_3 =l$
Substituting these values
$2(l^2 \alpha _1 \Delta T + l^2 \alpha _2 \Delta T)cos \theta -2 l^2 sin \theta d\theta=2l^2 \alpha _1 \Delta T + 2l^2 \alpha _1 \Delta T -2 l^2 \alpha _2 \Delta T$
$sin \theta d\theta = 2 \alpha _1 \Delta T (1 - cos \theta) - \alpha _2 \Delta T$
Substituting $\theta = 60^0$
$d \theta = \frac {2 (\alpha _1 - \alpha _2) \Delta T}{\sqrt 3}$