

(i) p-block elements $ns^2np^{1-8}$
(ii)d -block elements $(n-1)d^{1-10}ns^{1-2}$
(iii)f -block elements $(n-2)f^{1-14} (n-1)d^{0-1} ns^2$
(iv) Actinoids : $5f^{1-14} 6d^{0-1} 7s^2$
It is done to maintains its structure and to preserver the principle of the classificationn by keeping elements with the similar properties in a single column
Noble gases have a stable octet electronic configuration of ns2 np6 (except for helium, which has 1s2), making them highly resistant to gaining additional electrons. Their electron gain enthalpies are significantly positive because adding an electron would require it to enter a higher principal quantum level, resulting in a highly unstable electronic configuration. As a result, energy must be supplied to force an extra electron into the atom.
Mendeleev Periodic Law states that the properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic weights whereas Modern Periodic Law states that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers. Thus, the basic difference in approach between Mendeleev s Periodic Law and Modern Periodic Law is the change in basis of arrangements of elements from atomic weight to atomic number.
Isoloted Gaseous atom means that the atom should be free from other atoms in the gaseous state. No energy should be required to separate of further from other atoms. Ground state means the lowest energy state possible for that atom. These terms are used for comparison purposes
(i)Each one of these ions contains 10 electrons and hence all are isoelectronic ions,
(ii)The ionic radii of isoelectronic ions decrease with the increase in the magnitude of the nuclear charge. Among the isoelectronic ions: $N^{3-},O^{2-}, F^{ }, Na^{+}, Mg^{2+},Al^{3+}$
, nuclear charge increase in the order:
$N^{3-} < O^{2-} < F^{ } < Na^{+} < Mg^{2+} < Al^{3+}$
Therefore, the ionic radii decrease in the order:
$N^{3-} > O^{2-} > F^{ } > Na^{+} > Mg^{2+} > Al^{3+}$
The outermost electronic configuraton of nitrogen ($2s^2 2p_x^1 2p_y^1 2p_z^1$) is very stable because p-orbital is half filled. Addition of extra electron to any of the 2p orbital requires energy.
Oxygen has 4 electrons in 2p orbitals and acquires stable configuration i.e., 2p3 configuration after removing one electron.
After removing 1 electron from the sodium atom the ion formed acquires the configuration of inert gas, neon. The second electron is removed from one of the 2p-orbitals which are completely filled i.e., have a total of 6
electrons and are closer to the nucleus
It has completely filled valence shell and exhibit properties & characteristics of other noble gases
(i) The species O has the smallest Radius because the radius of anions is always larger than the radius of the atom from which it is formed.
(ii)$K^+$ has the smallest radius.In $K^+$, the outermost shell is third whereas in $Sr^{2+}$ itis fourth
(ii)Cl has the smallest radius .Si,P and Cl belongs to the same period .In a period atomic radius decreases with increase in atomic number due to increase in effective nuclear charge
1. (iii)
2. (ii)
3. (ii) and (iii)
4. (iii)
5. (iv)
6. (i)
7. (iii)
8. (iii)
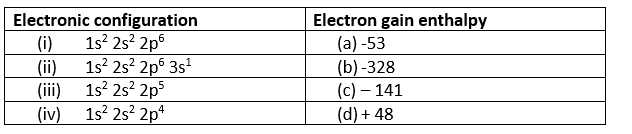
(i) -> (d); (ii) -> (a) (iii) -> (b), (iv) -> (c)