Class 12 Physics > Electric Charges and Fields (Chapter 1 Hub Page) > Electrical and Electrostatic Force
In this page, we will learn about electrical force, the definition of electric force along with a few examples. At the end of the page, we will also define electrostatic force.
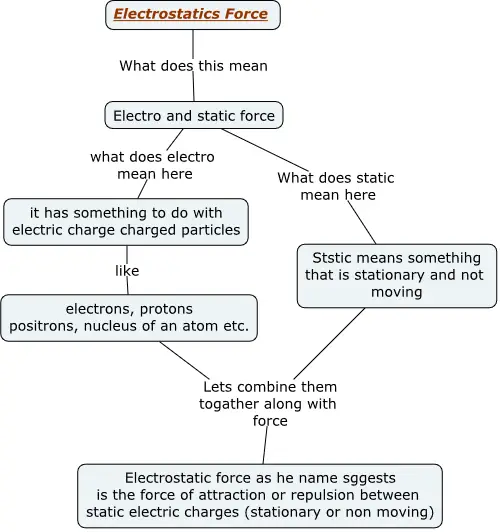
Electrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the study of electric charges at rest and the interactions between them.
The mutual influence between two charged particles placed near each other, without physical contact, is called electric interaction.
The force experienced by a charged particle due to the presence of another charged particle is called electric force.
The magnitude of electric force between two charged particles depends on the properties of the charges and the conditions of their surroundings.
The effect of a medium on electric force is described by a quantity called the dielectric constant or relative permittivity of the medium.

Electric force and gravitational force are both fundamental non-contact forces that act between particles without any physical contact.
| Electric Force | Gravitational Force |
|---|---|
| Acts between electric charges | Acts between masses |
| May be attractive or repulsive | Always attractive |
| Depends on the surrounding medium | Independent of the surrounding medium |
| Extremely strong at atomic scale | Very weak at atomic scale |
| Can cancel due to presence of opposite charges | Cannot be cancelled |
Qualitative ideas help us understand the nature of electric force, but they are not sufficient to calculate its exact magnitude in a given physical situation.
Coulomb’s law gives the mathematical expression for the electric force between two point charges at rest.
The simple description of electric force is valid only when certain physical conditions are satisfied.
Misconceptions about electric force often arise due to incomplete understanding of its properties.
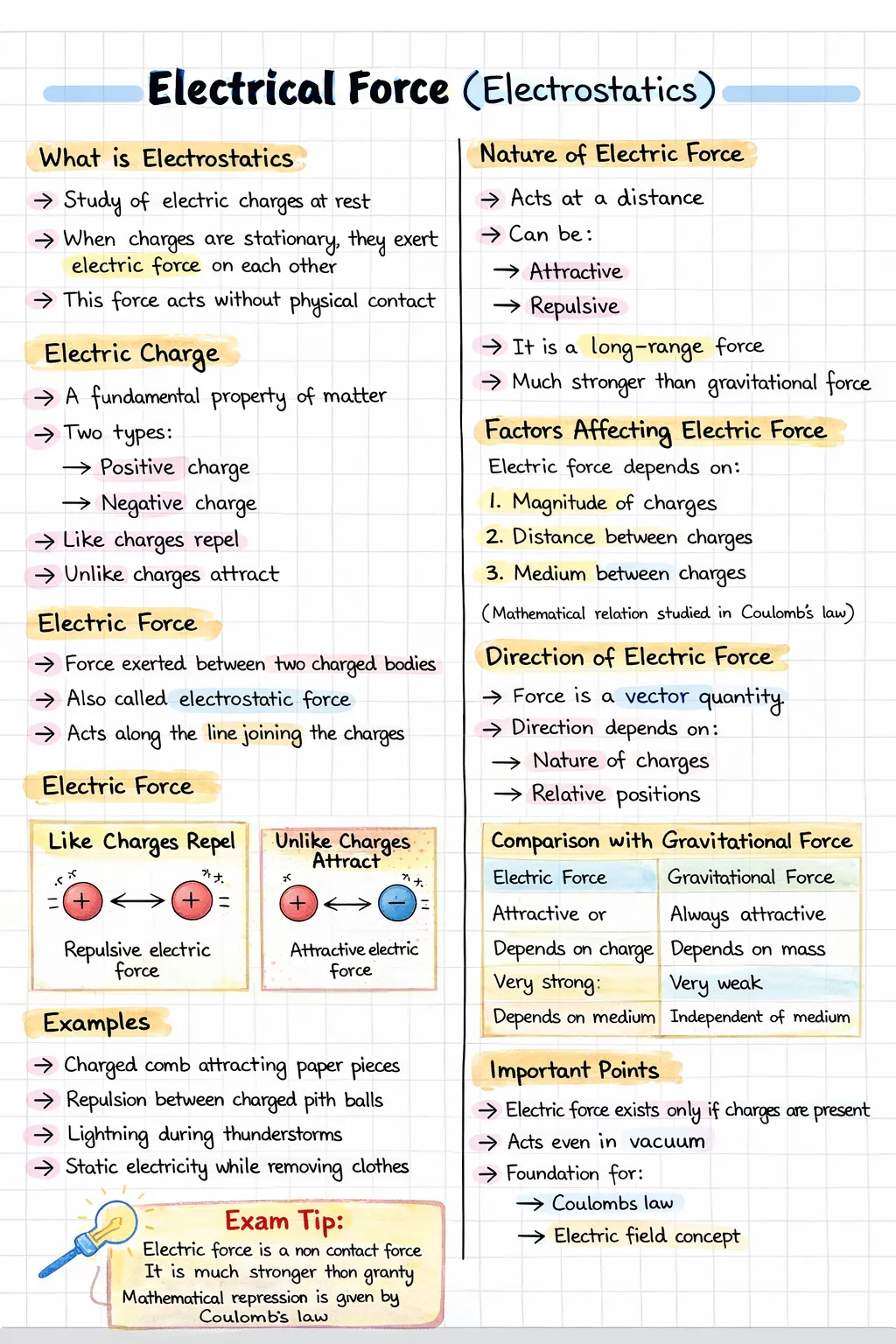
Figure below shows a concept map explaining what are electrostatic forces