Transistor as an oscillator
Transistor as an oscillator
- electronic oscillator is a circuit which converts DC energy with AC energy at very high frequency
- Oscillators generates alternating voltage when it is supplied energy from a DC source
- Figure below shows the representation of an oscillator and the basic parts of this circuit are
(a) An amplifier circuit
(b) An LC network
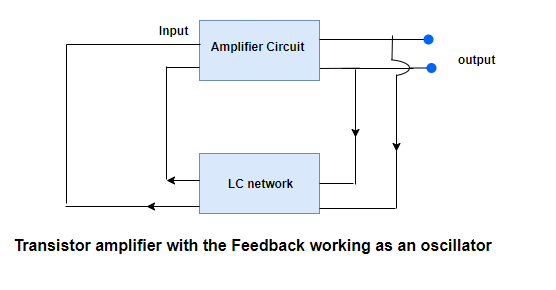
- Amplifier circuit is just a transistor used in CE mode and the LC network consist of a inductor and capacitor
- The resonance frequency of this circuit determines the frequency at which oscillator will oscillates and it is
$f_0= \frac {1}{2 \pi \sqrt {LC}}$
- In this circuit only batteries are used to bias the transistor and no other external signal is applied to the amplifier circuit
- The LC network is used as a feedback to fed a part of the output signal back to the input section
- This signal is again amplified by amplifier section and a part is again feedback to the input section and this makes it is a self sustained device
- Two important and necessary conduction for circuit oscillations are
(i) The feedback must be positive
(ii) Feedback factor must be unity i.e βA=1
- The circuit resonates at resonating frequency f0 and the output of the circuit acts a source of alternating voltage of this frequency
- This frequency can be charged by changing L or C
 Also Read
Also Read


