

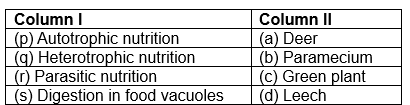
p->c
q -> a
r ->d
s -> b
Autotrophs are classified based on their source of energy. If they use the light energy of the sun, they are called photoautotrophs. If they use chemical energy of certain compounds such as ammonia and nitrites, they are called chemoautotrophs.
Chlorophylls and carotenoids are the two types of photosynthetic pigments.
Chlorophyll A and chlorophyll B are the two types of chlorophylls.
Answer
Carotene.
Radiant energy consists of both light and heat energy. The light energy is trapped into chlorophyll molecules and then used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen in order to release energy. The heat energy maintains the optimum.
Low light intensity lowers the rate of photosynthesis. As the intensity is increased the rate also increases. However, after reaching an intensity of 10,000 lux (lux is the unit for measuring light intensity) there is no effect on the rate. Very high intensity may, in fact, slow down the rate as it bleaches the chlorophyll.
The animals that take in large pieces of food are called macrophagous feeders. For example, hydra and sea anemone.
The animals that take in very small particles of food are called microphagous feeders. For example, earthworm and mussels.
Detritivores are those animals that feed on dead plant and animal bodies after breaking them into small pieces. The digestion takes place inside the body.
ex="-1">
An association between two organisms of different species is called symbiosis. ‘sym’ means together and ‘bio’ refers ti living thing. For example, cattle and egret, man and intestinal bacteria, etc.
ex="-1">
An association between two individuals where one is harmed and the other is benefited. The dependent one is called the parasite and the other one is called the host. For example, leech is an ectoparasite which sucks blood of the host, tapeworm lives in the digestive tract of man and causes disease.
Haustoria are specialized structures found in saprophytes that are used to draw nutrients directly from the vascular system of the host. They are modified roots. For example, in Cuscuta.
ex="-1">
Feeding on faeces is called coprophagy.
ex="-1">
The organisms that feed on decomposing animal bodies are called carrion feeders.
ex="-1">
The plants that trap and feed on insects are called insectivorous plants. These plants do have photosynthetic apparatus. However, they grow in nitrogen-deficient soil and hence, feed on insects to meet this deficiency. For example: pitcher plant, sundew, venus fly catcher.
ex="-1">
The two sets of teeth in a man are the milk teeth and the permanent teeth. Milk teeth are first to appear and are only 20 in no. they start falling y the age of 5 and are replaced by permanent teeth which are 32 in number.
ex="-1">
(i) saprophytes- Mucor, yeast
(ii)saprozoans- chilomonas, Mastigamoeba
Nutrients are various organic and inorganic substances required by the organism to carry out their functions.
The process by which the organisms synthesis their own food using carbon dioxide and water is called autotrophic nutrition. For example, green plants, sulphur bacteria, etc.
The process of nutrition where the organisms obtain their food from other organisms. For example, most of the bacteria, fungi and all animals. They are all dependent on autotrophs directly or indirectly.
The green plants trap the sun’s energy and the raw materials in food molecules. They form the basis of sustenance for all the organisms directly or indirectly. They are also called the producers as they produce food for all other organisms.
Photosynthesis is a process which utilizes carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll to synthesize carbohydrates like glucose.
Photosynthesis requires the radiant energy of the sun, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, water and minerals.
Many processes like respiration, combustion, volcanic activity, etc. release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This carbon dioxide of the atmosphere is used by the terrestrial plants and the hydrophytes use the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water.
Water is absorbed by the roots of the green plants from the surrounding soil.
Minerals like magnesium form essential compounds such as chlorophyll. Hence, they are important for photosynthesis.
Plants obtain the minerals from the soil by their dissolution in water.
Carbon dioxide is obtained from the atmosphere through the stomata that are present on the leaves. Water is drawn from the soil by the root of the plant and then transported to the leaves through the vascular bundles.
Heterotrophic nutrition is broadly classified as holozoic, saprotrophic and symbiotic.
The nutrition that involves the taking in of solid or liquid (in case of fluid feeders) particles of food which have to be further broken down into simpler particles inside the organism. These particles may be big or small.
Saprotrophs are organisms that feed on dead and decaying matter. They secrete substances that decompose the dead matter and then take in the food. For example: Rhizopus, musroom, etc.
(i) Cuscuta
(ii)Viscum
Amoeba shows holozoic nutrition. Its diet includes bacteria, microscopic plants like the diatoms, minute algae, and microscopic animals like other protozoa, nematodes and even dead organic matter.

The various nutrients carry out different functions such as
i. Energy production
ii.Synthesis of materials for growth and repair of tissues
iii.Synthesis of materials for carrying out and maintaining life functions
iv. Synthesis of materials for immune system.
The reactants of photosynthesis are:
Carbon Dioxide: During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is converted into carbohydrates and this is called fixing of carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide of the atmosphere is used by the terrestrial plants whereas the hydrophytes use the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water.
Water: During photosynthesis, hydrogen of water is used to fix carbon dioxide and its oxygen is released. Water is obtained through the root hairs by absorption.
Chlorophyll: They are pigments capable of absorbing radiant energy of the sun. There are two types of photosynthetic pigments- chlorophyll and carotenoids. Chlorophyll is the main pigments as they are involved in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy. The carotenoids also absorb light energy but they pass it to the chlorophyll molecules.
Radiant Energy: The radiant energy from the sun is the source of both light and heat energy for photosynthesis. Light energy is harvested by the pigments in order to carry out the breaking down of water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen. The temperature required by the enzymes to function is maintained by the heat energy of the sun.
Minerals like magnesium are essential as they form the structure of the pigment molecules. Minerals are obtained through water on form of dissolved salts.
The green plants are fed on by the herbivores which in turn by carnivores. Ultimately, the decomposers derive their nutrition from the dead plants and animals. Thus, all organisms are directly or indirectly dependent on the green plants.
Holozoic nutrition involves the following steps:
Absorption is taking in of digested food by cells and tissues. This involves the absorption of food in the soluble form from the region of digestion into the tissues or in to where it has to be utilized or into the blood stream which transports it to the different tissues. This takes place through the cell membranes. The absorption may be passive or active. Passive absorption is through diffusion or osmosis without using energy. For example: Water is absorbed by osmosis. Active absorption needs energy. For example, absorption of glucose and sodium ions.
Amoeba is a protozoan and holozoic. Since it is a unicellular organism, the digestion is intracellular. The food taken in remains in a food vacuole or gastric vacuole formed by the cell membrane and a bit of the cytoplasm. The vacuoles are transported deeper into the cells by cytoplasmic movements. Here they fuse with lysosomes that contains enzymes such as amylase and proteinase. Thus, amoeba can digest sugar, cellulose and protein. Fats, however, remain undigested.
The first portion of the small intestine, the duodenum gets the pancreatic and the bile juice. The chyme is acted upon by the enzymes and salts present in these two secretions. The starch is converted into maltose by the pancreatic amylase and the remaining proteins, proteoses and peptones into peptides are converted and amino acids by trysin. The bile juice emulsifies the fats and then converts them into fatty acids and glycerol by the action of lipase.
In jejunum, there is no digestion. In ileum, the food is completely broken down into the simplest of forms e.g. proteins into amino acids and carbohydrates into monosaccharides. This digested mass is now called the chyle and it is in a liquid form.
Functions of the large intestine are:
25. Liver carries out the following after the digested food reaches the liver through the blood stream:
Two types of digestion are:
Mechanical: Mechanical digestion involves grinding of food into smaller particles by the teeth.
Chemical: Chemical digestion involves treatment of food by enzymes and breaking them into the simplest form in which they can be easily dissolved and then absorbed by the body.
Those organisms that synthesize food with the help of the light energy of the sun, carbon dioxide and water are called photoautotrophs. The process of synthesis of food in this manner is called photosynthesis.
For example-
cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria, prokaryotes), algae and all green plants.
The various factors affecting photosynthesis are:
Parasites may be classified as:
Paramecium has a specific oral apparatus. Its oral groove consists of cilia which produce water currents. Only micro food particles reach cytopharynx through the cytostome along with the water current. When cytopharynx is full with food vacuole which pinches off from the cytopharynx and gets ingested.
The digestive glands in human digestive system are present outside the digestive tract and within the tract.
Outside the digestive tract Salivary glands the main salivary glands are:
This Class 10 Nutrition | Life processes Important questions with answers is prepared keeping in mind the latest syllabus of CBSE . This has been designed in a way to improve the academic performance of the students. If you find mistakes , please do provide the feedback on the mail.