Solved Example
Question 1
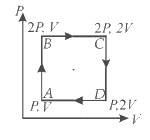
A ideal monatomic gas is taken through the process ABCDA as shown in below P-V diagram. Calculate the Work done by gas
 Solution
Solution
Work done by the gas from A to B = 0 ( as volume constant and area enclosed by AB is zero)
Work done by the gas from B to C = 2PV ( Area enclosed by line BC)
Work done by the gas from C to D = 0 ( as volume constant and area enclosed by AB is zero)
Work done by the gas from D to A = -PV ( Area enclosed by line BC and negative as volume is decreased)
Net Work Done = 2PV - PV = PV
Question 2
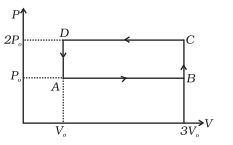
An ideal gas undergoes cyclic process ABCDA as shown in given P-V diagram .The amount of work done by the gas is
 Solution
Solution
Work done by the gas from A to B = 2PV ( Area enclosed by line AB)
Work done by the gas from B to C = 0 ( as volume constant and area enclosed by BC is zero)
Work done by the gas from C to D = -4PV ( Area enclosed by line CD and negative as volume is decreased)
Work done by the gas from D to A = 0 ( as volume constant and area enclosed by DA is zero)
Net Work Done = 2PV - 4PV = -2PV